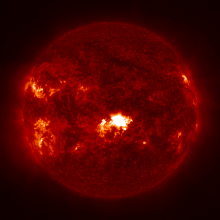
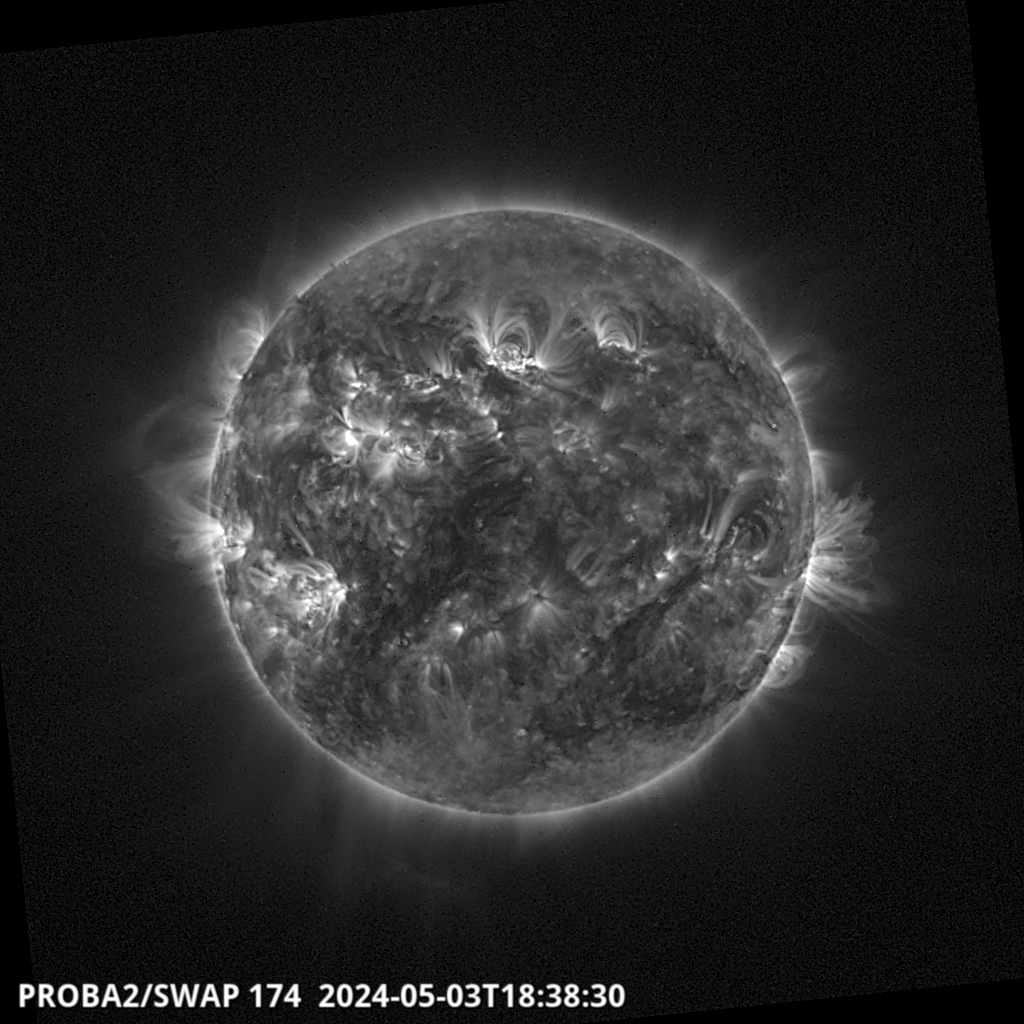
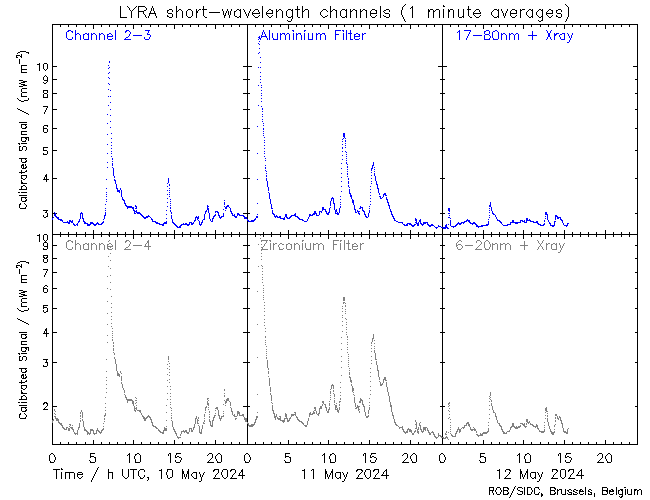
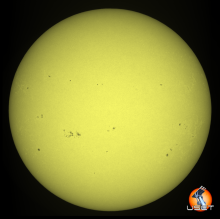
The solar flaring activity was at moderate level during the last 24 hours, with few C-class flares and two M-class flares. The strongest flare was GOES M1.7 flare from NOAA active region (AR) 3761 which peaked at 04:42 UTC on Jul 26. During the flare, the source region (AR 3761) of the flare had beta-gamma configuration of its photospheric magnetic field. Currently, NOAA AR 3762 is the most complex region on the disk (beta-gamma-delta magnetic field configuration), but it has only produced C-class flarings. The solar flaring activity is expected to be at moderate to high levels over the next 24 hours, possibly with few M-class flares and a low chance for isolated X-class flares.
No Earth-directed CMEs were detected in the available coronagraph observations during the last 24 hour.
The greater than 10 MeV GOES proton flux was below the threshold level over the past 24 hours. It is expected to remain so during the next 24 hours. A major flare from NOAA active regions which are presently close to and at the W limb, in the coming hours, could be possibly associated with a proton event.
The greater than 2 MeV electron flux, as measured by the GOES-16 satellite, was below the threshold level over the past 24 hours and is expected to remain so in the coming 24 hours. The 24h electron fluence is presently at low level, and it is expected to be at low to normal level in the next 24 hours.