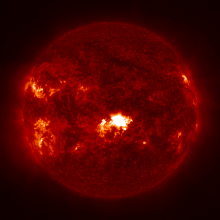
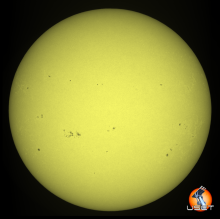
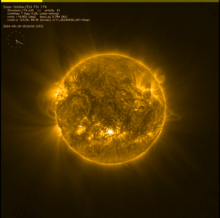
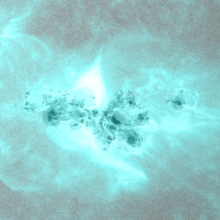
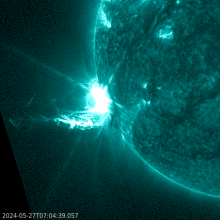
Old NOAA 3738 produced a very strong X-class flare late on 22 July. Solar Orbiter's STIX instrument indicates this might have been an X14 flare. The associated CME is heading away from Earth, towards Solar Orbiter. ***UPDATED***
SIDC News
Preliminary sunspot numbers during last week were the highest in 22 years.
On 20 May, instruments on board Solar Orbiter observed what was most likely the strongest solar flare so far during SC25.
An impressive eruption took place over the Sun's southwest limb on 24 June.
The Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (JSWSC) opens a Topical Issue "Severe space weather events of May 2024 and their impacts".
The fairly recent Hpo geomagnetic index deals with the two major shortcomings of the Kp index.
The STCE's SC25 Tracking page has been updated to reflect the latest evolution of some critical space weather parameters for the ongoing solar cycle 25 (SC25).
The Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (JSWSC) opens the Topical Issue “Swarm 10-Year Anniversary”, dedicated to new results from ESA’s Swarm mission, in particular to investigations of the Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Coupling, Ionospheric and Thermospheric processes, and their implications for Space Weather.
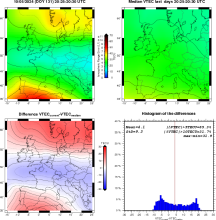
Important ionospheric effects over Europe have been observed during the extreme geomagnetic storm of 10 and 11 May.
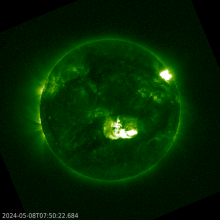
Returning old active region NOAA 3664 produced an X2.8 flare on 27 May. Updates on further activity from this region will be posted here. ***UPDATED (8)***
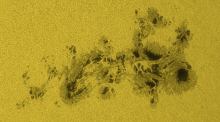
Flare productivity from NOAA 13664 and the extreme geomagnetic storm on 10-11 May rank amongst the most impressive in the space weather domain. A perspective.